
The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 governs the laws relating to gratuity in India. In this article, I have tried to answer the generic queries which the professionals come across in day to day work.
1) Under what circumstances is gratuity payable to an employee?
a) Gratuity is payable to an employee, only if he or she has completed five years of service, and the employment is discontinued as a result of superannuation, resignation, termination or any other reason.
b) However, in case of death or disablement, gratuity is payable even if the employee has not completed five years of continuous service
c) In other words, gratuity is not payable to an employee while in service, even if he has completed five years of service
2) How to determine whether an employee has completed five years of continuous service?
In order to determine whether the employee is eligible for gratuity, continuous service of five years has to be established. In case of anomaly due to break in service or sabbatical or long leave, employee will be said to be in continuous service for that year if he has worked for minimum days as per the table below –
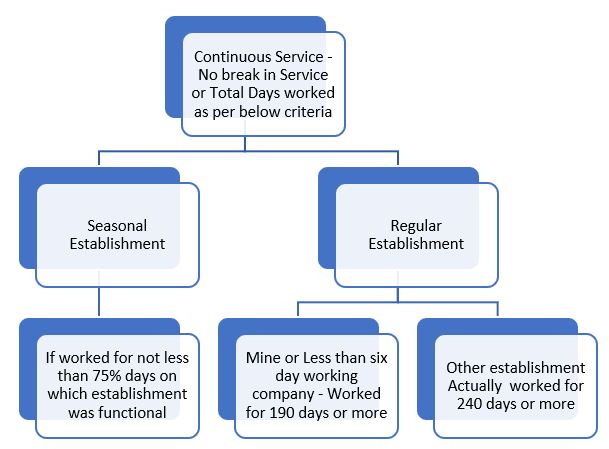
For above calculation, if employee has been absent due to layoff, paid leave, maternity leave, it will be counted for calculating actual days worked
3) How is the gratuity calculated?
a) Identify Last drawn basic wages * 15/26 * No of Years of Continuous Service
b) No of Years will be rounded off to the nearest whole number, for example, if employee worked for 5 years 5 months and 20 days, it will be counted as 5 years, whereas if employee worked for 5 years six months and 5 days, it will be counted as 6 years
c) Maximum gratuity payable is Rs 20 lakhs.
4) Is gratuity liable to tax in the hands of employee or is it tax- exempt?
a) Gratuity paid as per the Payment of Gratuity Act is completely exempt in the hands of the employee, subject to maximum of Rs 20 lakhs. Any excess amount is taxable.
b) Thus, if an employer voluntary pays an employee who has completed only 4 years of service, the amount will be taxable as it is not gratuity as per Payment of Gratuity Act
5) Is it a fair practice to include gratuity in CTC or to deduct monthly amount from the monthly salary and create provision for employee’s gratuity?
a) Gratuity, as per the statute is a gratuitous payment by the employer for continuity and commitment by the employee. Hence, the amount should be paid by the employer over and above the regular compensation package
b) Further, practice of deduction is not suggested as it is a contingent payout subject to fulfilment of conditions and hence mandatory deduction from monthly payout is not suggested
6) Can the gratuity be forfeited, if so, under what circumstances?
Gratuity is not payable to an employee if
i) His services are terminated for any act, wilful omission, or negligence causing any damage or loss to or destruction of property of the employer to the extent of damage so caused
ii) His services are terminated for any act involving moral turpitude, rioutous or violent acts, provided such acts are committed during the course of employment
7) In case an employee is transferred from one firm / entity to another of the same group, then what are the implications
a) If the employee is transferred from one company to another within the same group, at the behest of employer, the services so rendered in the previous organisation will be counted for gratuity entitlement
b) Thus, an employer cannot escape gratuity liability by regularly shifting an employee from one firm to another before five years of service
8) Is there any deadline for payment of Gratuity to an eligible employee ?
a) The gratuity should be paid within 30 days of become liable
b) In case of delay, the employer is liable to pay Interest on the same at simple interest rate as specified by the government from time to time
9) What are the amendments expected under Labour Codes?
As per Chapter V of Social Security Code, 2019, the law relating to gratuity is constant except for following additional changes
a) Employees on fixed term contract will be eligible for gratuity irrespective of completion of five years of service
b) The calculation of gratuity may vary because of new definition of ‘wages’ and the same may increase if the current Basic + DA is below 50% of gross salary
c) It is stipulated that each organisation has to avail the insurance policy to cover the gratuity cost mandatorily
2 thoughts on “GRATUITY – Technicalities Explained”